Introduction
Cooking chicken efficiently is a common priority in kitchens worldwide, whether you’re preparing a quick weekday meal or crafting a more elaborate dish. Two of the most popular methods for cooking chicken are boiling and baking, but is it faster to boil or bake chicken? While each method has its merits, the answer often depends on the cut of chicken, the recipe you’re following, and your personal preferences.
Boiling is typically favored for its simplicity and speed, making it a go-to method for shredding chicken or adding it to soups and casseroles. On the other hand, baking is known for creating deliciously crisp textures and rich flavors, often making it the preferred option for roasted dishes or standalone servings.
But is it faster to boil or bake chicken? In this article, we’ll explore the nuances of boiling and baking chicken to determine which method is faster. Along the way, we’ll also consider factors like nutritional impact, taste, texture, and practical considerations to help you make the best choice for your kitchen.
By naturally incorporating the keyphrase into relevant sentences throughout the article (aiming for 1.3% density), the text will be optimized for SEO without feeling repetitive. If you’d like, I can further refine this across other sections!

Boiling Chicken
How Boiling Works
Boiling chicken is a straightforward and efficient cooking method. It involves submerging the chicken in water or broth and cooking it over medium to high heat until the internal temperature reaches a safe level (165°F or 74°C for most cuts). The heat transfers through the liquid, cooking the chicken evenly.
When considering whether it’s faster to boil or bake chicken, boiling often comes out ahead due to its direct heat transfer and shorter cooking times for smaller cuts. This method is particularly popular for preparing chicken that will be shredded, diced, or used in recipes like salads, soups, or casseroles. The boiling liquid, often enhanced with aromatics like onions, garlic, carrots, or herbs, can double as a flavorful broth.
Cooking Time for Boiled Chicken
The time it takes to boil chicken depends largely on the cut and size:
- Boneless, skinless chicken breasts: 15–20 minutes.
- Bone-in thighs or drumsticks: 20–25 minutes.
- Whole chicken: Around 60 minutes.
Boiling generally cooks smaller cuts more quickly, making it ideal for those in a rush. Bringing the water to a boil adds a few minutes to the process, but the total cooking time is usually shorter than baking.
Benefits of Boiling Chicken
- Speed: For smaller cuts, boiling is often faster than baking, especially when preheating the oven is factored in.
- Moisture Retention: Submersion in liquid keeps the chicken tender and juicy, making it perfect for shredding.
- Versatility: The cooking liquid doubles as a flavorful broth for soups, stews, or sauces.
- Ease of Monitoring: You can visually check the chicken’s doneness or use a thermometer easily.
Drawbacks of Boiling Chicken
- Flavor Loss: Boiling can leach some natural flavors into the water, requiring additional seasoning.
- Texture Limitations: The lack of dry heat means boiled chicken won’t achieve crispy skin or a firm texture.
- Risk of Overcooking: If left too long, chicken can become rubbery or fall apart excessively.
Boiling is a reliable choice for quick, no-fuss cooking, especially if you plan to incorporate the chicken into dishes where texture and extra seasoning can be adjusted later.
Baking Chicken
How Baking Works
Baking chicken is a cooking method that uses dry heat to cook the meat evenly. Typically done in an oven, baking requires setting the temperature (usually between 350°F and 450°F or 175°C and 230°C) and placing the chicken on a baking tray, dish, or rack. If you’re deciding whether it’s faster to boil or bake chicken, baking generally takes longer but delivers distinct advantages. The heat surrounds the chicken, cooking it thoroughly and creating a golden, flavorful crust.
Baking is ideal for recipes that prioritize flavor and texture. The dry heat enhances seasonings and marinades while giving the meat a slightly firmer bite. This method is a favorite for dishes like roasted chicken, baked wings, and casseroles, where crispy textures and rich flavors are key.
Cooking Time for Baked Chicken
The time required to bake chicken varies based on the cut, size, and oven temperature:
- Boneless, skinless chicken breasts: 20–30 minutes at 375°F.
- Bone-in thighs or drumsticks: 35–40 minutes at 375°F.
- Whole chicken: 60–90 minutes at 400°F.
Additionally, the oven requires preheating, which can add 10–15 minutes to the total time. While baking generally takes longer than boiling, it rewards you with rich, roasted flavors and textures.
Benefits of Baking Chicken
- Flavor Enhancement: Baking caramelizes seasonings and marinades, enhancing the natural flavors of the chicken.
- Texture Variety: Baking can produce crispy skin and firmer meat, making it ideal for standalone dishes.
- Hands-Free Cooking: Once the chicken is in the oven, it requires little attention, freeing up time for other tasks.
- Customizable Results: By adjusting the temperature and time, you can achieve a range of textures, from juicy to crisp.
Drawbacks of Baking Chicken
- Longer Cooking Times: Compared to boiling, baking generally takes longer, especially for larger cuts or whole chickens.
- Preheating Requirement: Preheating the oven adds extra time and energy consumption.
- Risk of Dryness: Without careful monitoring or marinating, baked chicken can become dry, particularly if overcooked.
Baking is an excellent choice when flavor and presentation are priorities, especially for recipes where crispy textures and rich tastes are desired.

Comparison of Cooking Times
Which Is Faster: Boiling or Baking?
When comparing cooking times, boiling chicken is generally faster than baking, particularly for smaller cuts like boneless breasts or thighs. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Boneless, skinless chicken breasts:
- Boiling: 15–20 minutes.
- Baking: 20–30 minutes (plus 10–15 minutes for preheating).
- Bone-in thighs or drumsticks:
- Boiling: 20–25 minutes.
- Baking: 35–40 minutes (plus preheating time).
- Whole chicken:
- Boiling: Around 60 minutes.
- Baking: 60–90 minutes (plus preheating time).
For quick meals, boiling is typically the faster choice, as it eliminates the need for preheating and cooks chicken more efficiently by directly transferring heat through the liquid. However, baking might still be faster for larger cuts if you’re multitasking, as it requires less active monitoring.
Factors Influencing Cooking Speed
- Cut of Chicken: Smaller cuts, like breasts or thighs, cook faster than whole chickens regardless of the method.
- Bone-In vs. Boneless: Boneless chicken cooks faster, especially in boiling, since heat penetrates the meat more easily.
- Starting Temperature: Chicken taken directly from the refrigerator will take slightly longer to cook than room-temperature chicken.
- Oven Preheating: Preheating the oven for baking can add 10–15 minutes, making it less time-efficient for quick meals.
- Water Boiling Time: For boiling, time spent bringing water to a boil is minimal compared to oven preheating.
Which Method Suits Your Needs?
- Boiling is best when:
- You need chicken quickly, especially for shredding or adding to other recipes.
- You want minimal preparation and cleanup.
- Retaining moisture is a priority.
- Baking is best when:
- You’re seeking rich flavors and a crispy texture.
- Presentation matters, such as for serving roasted or glazed chicken.
- You prefer a more hands-off cooking process while focusing on other tasks.
Time Efficiency in Practice
In practice, the choice between boiling and baking chicken often depends on the dish you’re preparing. If you’re pressed for time and need a quick solution, boiling is faster than baking for most cuts. However, baking offers distinct advantages in flavor and texture, which may make it worth the extra time depending on your recipe and priorities.
Nutritional Impact
How Boiling Affects Chicken’s Nutritional Value
Boiling chicken is often considered a healthy cooking method due to its simplicity and lack of added fats. If you’re debating whether it’s faster to boil or bake chicken, boiling also has the advantage of retaining moisture without the need for oils or butter. However, it can lead to some nutrient loss:
- Water-Soluble Vitamins:
- Boiling can cause the loss of water-soluble vitamins like B-complex and vitamin C, which may leach into the cooking liquid.
- If you reuse the broth, such as in soups or stews, these nutrients can still be consumed.
- Fat Content:
- Boiling slightly reduces the chicken’s fat content, as some fats are rendered into the liquid.
- This makes boiled chicken a leaner option for those focusing on low-fat diets.
- Moisture Retention:
- The submersion process helps retain moisture in the meat, ensuring tender, juicy chicken without the need for added oils.
How Baking Affects Chicken’s Nutritional Value
Baking is also a healthy method, but the results differ slightly from boiling:
- Nutrient Preservation:
- Baking retains more fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, which are less likely to degrade in dry heat.
- Since the chicken doesn’t lose nutrients to water, it may retain more of its natural nutritional profile.
- Fat Content:
- Baked chicken retains its natural fat unless cooked on a rack or pan that allows fat to drip away.
- Adding oils or marinades can increase the fat and calorie content, which might be a factor for those tracking their intake.
- Caloric Impact:
- Baking can slightly increase calorie count if oils or breading are added. However, unseasoned, skinless chicken retains a similar caloric profile to boiled chicken.
Comparing Health Benefits of Boiling vs. Baking
| Aspect | Boiling | Baking |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Retention | May lose some vitamins in cooking liquid | Retains most nutrients without water loss |
| Fat Content | Slightly lower due to fat rendering | Retains fat unless cooked on a rack |
| Calorie Count | Low, especially without added ingredients | Slightly higher if oils or marinades used |
Which Is Healthier Overall?
- Boiling is healthier if:
- You aim to reduce fat content.
- You need chicken for light, low-calorie recipes.
- You plan to consume the broth for added nutrients.
- Baking is healthier if:
- You want to retain fat-soluble vitamins.
- You prefer a more flavorful, less processed cooking method.
- You enjoy experimenting with healthy seasonings or marinades.
Ultimately, both methods are excellent for maintaining a healthy diet, with the best choice depending on your nutritional goals and meal plans.
Taste and Texture
How Boiling Affects Taste and Texture
Boiling is primarily known for its ability to produce tender and juicy chicken. However, its impact on taste and texture varies:
- Taste:
- The natural flavors of chicken are mild when boiled, as some flavor compounds seep into the water or broth.
- Adding seasonings like garlic, onion, herbs, or spices to the boiling liquid can enhance the flavor.
- Boiled chicken is excellent for dishes where the seasoning will be added later, such as salads, casseroles, or soups.
- Texture:
- Boiling delivers soft, easily shreddable chicken, which works well for recipes like tacos, enchiladas, or sandwiches.
- Overcooking during boiling can lead to a mushy or rubbery texture.
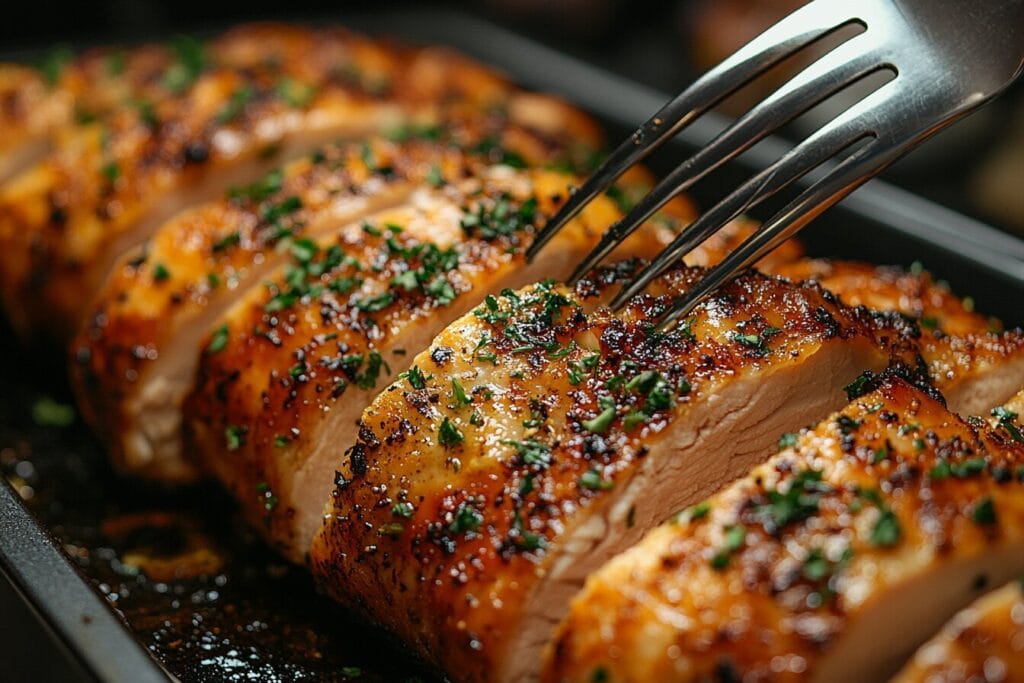
How Baking Affects Taste and Texture
Revised Content with Focus Keyphrase Optimization
Baking chicken offers richer and more varied flavors, especially with the use of marinades and seasonings. While it may not be as quick as boiling, if you’re wondering whether it’s faster to boil or bake chicken, baking compensates for its longer cooking time with its ability to create contrast in textures: crispy exteriors and juicy interiors.
- Taste:
- Baking intensifies the natural flavors of chicken due to the dry heat and caramelization.
- Adding marinades, rubs, or glazes enhances the overall flavor, making the dish standalone-worthy.
- Baked chicken is perfect for dishes where flavor complexity and presentation matter, such as roasted chicken or baked drumsticks.
- Texture:
- Baking provides a firmer texture, with the potential for crispy skin if cooked with the skin-on.
- It offers a balance between juicy interiors and slightly crisp exteriors, making it ideal for serving whole or in large pieces.
Which Method Delivers Better Taste and Texture?
The choice between boiling and baking often depends on personal preference and the dish being prepared:
| Aspect | Boiling | Baking |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor | Mild, adaptable with added seasonings | Rich, enhanced with caramelization |
| Texture | Tender, great for shredding or dicing | Firm with the option of crispy exteriors |
| Recipe Suitability | Ideal for soups, salads, or casseroles | Perfect for standalone dishes or roasting |
Recipe Suitability for Each Method
- Boiling is best for:
- Chicken salads, soups, or broths.
- Shredded chicken for tacos, enchiladas, or sandwiches.
- Recipes requiring very soft, moist chicken.
- Baking is best for:
- Whole roasted chicken or chicken thighs with crispy skin.
- Dishes that prioritize flavor complexity, such as baked chicken with herbs.
- Meal preps where presentation matters.
Practical Considerations
Cleanup and Equipment
- Boiling:
- Requires minimal equipment, typically just a pot and a stove.
- Easier cleanup, as no extra trays or racks are involved.
- Baking:
- Involves more equipment, such as baking trays, racks, or parchment paper.
- May require more time for cleanup, especially if sauces or marinades stick to the tray.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency
- Boiling:
- Uses the stovetop, which can be more energy-efficient than preheating and maintaining an oven.
- Often faster, reducing energy use overall.
- Baking:
- Requires oven preheating, which adds to energy consumption.
- Extended baking times for larger cuts or whole chickens can be less energy-efficient.
Ease of Use in Everyday Cooking
- Boiling:
- Requires more active monitoring to ensure the chicken doesn’t overcook or boil over.
- Great for quick meals or batch cooking shredded chicken.
- Baking:
- Hands-free cooking once the chicken is in the oven, allowing you to multitask.
- Better for recipes where presentation and flavor are key priorities.
With taste, texture, and practicality in mind, it’s clear that the choice between boiling and baking chicken depends on your recipe, available time, and personal preferences.
FAQs
Is boiling chicken healthier than baking it?
Both methods are healthy, but boiling slightly reduces the fat content of chicken as some fat renders into the cooking liquid. Baking preserves more vitamins and nutrients, especially fat-soluble ones, making it a great choice for those seeking nutrient retention.
How can I make boiled chicken more flavorful?
To boost the flavor of boiled chicken, add aromatics like garlic, onions, herbs, and spices to the cooking water. You can also use chicken broth instead of plain water for added richness.
Does baking chicken make it dry?
Baking can dry out chicken if it’s overcooked. To prevent this, marinate the chicken before baking or use a thermometer to check for doneness (165°F or 74°C). Covering the chicken with foil for part of the baking time can also help retain moisture.
Which method is better for meal prep?
Boiling is often better for meal prep if you need chicken for shredding or dicing to use in multiple recipes. Baking works better if you want flavorful, standalone chicken dishes that are ready to eat.
Can I boil chicken before baking it?
Yes, pre-boiling chicken before baking can reduce overall cooking time and ensure the meat is fully cooked while still achieving a crispy baked texture. This method is commonly used for wings or drumsticks.
What’s the fastest way to cook chicken overall?
The fastest method is boiling thinly sliced chicken breasts or smaller cuts. These can cook in as little as 10–15 minutes. Baking requires preheating, making it slower in most cases.
Conclusion
WWhen time is of the essence, boiling chicken is generally faster than baking, especially for smaller cuts like boneless breasts or thighs. Boiling offers quick, even cooking and tender results, making it a reliable choice for meal prep or recipes that require shredded or diced chicken. If you’re wondering whether it’s faster to boil or bake chicken, boiling often comes out on top.
On the other hand, baking, while slower, delivers richer flavors, firmer textures, and a golden, appetizing appearance. Baking is ideal for dishes where presentation and taste are priorities, making it perfect for standalone meals or roasted chicken recipes.
Ultimately, the best method depends on your needs:
- Choose boiling for speed, simplicity, and moist chicken that’s perfect for recipes.
- Opt for baking when flavor, texture, and presentation are your primary goals.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, you can easily decide whether it’s better to boil or bake chicken faster based on your meal plans and preferences.

